Some media may have led you to believe that dental care for people with diabetes is unaffected by the disease. Nevertheless, in matters of health, there can often be substantial disparities between the intended meaning and the actual comprehension. Dealing with diabetic patients for their dental issues is one of these concerns.
As long as the patient meets required conditions and certain limits are not exceeded dental treatments for diabetics are permitted. With all of this data in hand, it's time to dive into the importance of diabetic dental treatments.
The significance of dental care for diabetics
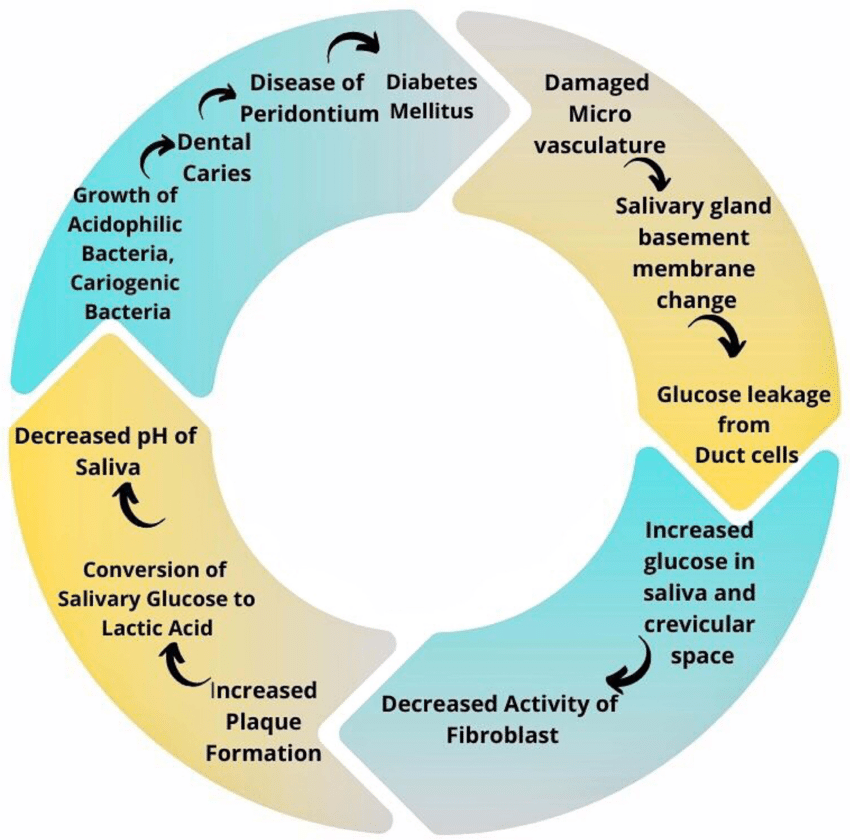
Patients with diabetes are at increased risk for developing complications such as delayed healing of dental abscesses and an increase in blood sugar levels due to a compromised immune system. Plaque buildup on teeth, cavities, and gum disease are all consequences of lack of saliva, which makes it harder to clean the mouth.
In diabetics, sugar damages tiny blood vessels, which in turn causes nutritional deficiencies in certain areas. Unnourished gums are more likely to get inflamed, which makes it hard for them to heal.
Diabetics can develop major oral health issues, including gingivitis if left untreated. For them, surgical treatment is the only viable cure to prevent advanced gingivitis. Diabetics must have good dental care, particularly for bad fillings, crooked teeth, gum irritation, poorly built crowns, and dentures that can make chewing uncomfortable. Improper chewing patterns in diabetic people contribute to excessive food consumption.
Tips for diabetic dental patients
Elevated blood glucose levels contribute to the delayed healing of injuries and inflammations in patients. These patients are at a higher risk for complications during complex dental treatments such as implants, All-on-Four, and other jaw surgeries. Key dental treatment criteria for diabetic patients are listed below.- Morning appointments are the best time to treat diabetic patients.
- Long wait times are unacceptable for patients with diabetes.
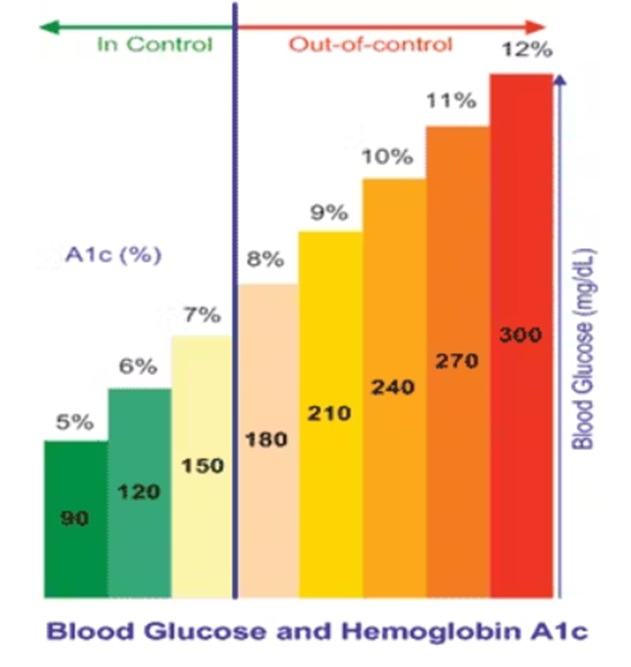
- Those with blood sugar levels over 180 mg are not eligible for comprehensive dental treatments.
- In case of emergency interventions in these patients, the patient is kept under close control and drug treatment for 48 days.
- Epinephrine-containing anesthetics should be avoided when getting dental work done under its influence.
- Surgical operations requiring general anaesthesia and lasting longer than two hours are classified as major surgeries. In such a situation, it is important to assess the patient's kidney and liver function and treat any electrolyte imbalances that may be present.
- If treatment is prolonged, blood glucose values should be monitored hourly.
Post-treatment considerations for diabetic patients:
Diabetic patients must be given special attention before and after dental treatment to ensure a speedy recovery. In addition to the risk of infection, patients with diabetes may develop syndromes such as dry mouth, decreased sense of taste, and malnutrition. Here are some important considerations for diabetic patients regarding oral care after treatment.
Applications that Increase Silvia
- Chewing Xylitol gum three times a day for 20 minutes.
- Salivary stimulants and hydrating agents.
- Formulations containing sodium carboxymethyl.
Applications to Prevent Bacterial Plaque
- Oral hygiene training
- Alcohol-free antiplaque and anti-tartar mouthwashes.
- Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine (not to exceed 14 days)
Applications that increase remineralization capacity
- Gels and mouthwashes containing fluoride.
- Medications that include calcium phosphate...
- Xylitol gums
Applications for Nutrition
- Oral hygiene procedures should be conducted consistently, including after consuming snacks.
- It is advisable to consume foods that are high in fibre and have a low glycemic index.
- Sugar alcohols like sorbitol, xylitol, and mannitol, as well as fermentable foods like these, contain calories that can be used as sweeteners; these should be consumed under medical supervision.
- There are sweetener alternatives available for diabetics that do not break down or contain calories. Some options include saccharin, aspartame, or sodium silicamate.
Diabetic patients should have good dental care to maintain a balanced diet and avoid complications during complex dental treatments. After treatment, it is important to provide diabetic patients with special care to avoid infection, dry mouth, reduced taste, and malnutrition.
