
Gingival abscess is a serious dental problem faced by 10-15% of adults worldwide. According to studies, untreated dental abscesses can increase the risk of spreading the infection to other parts of the body by up to 30%, while life-saving measures can be taken in 5 minutes in cases requiring emergency intervention. In this article, you can explore all aspects of gum abscess, starting with the definition, its development mechanisms, early symptoms, treatment methods, and precautions that can be applied at home.
What is a gum abscess?
A gum abscess is a localized accumulation of pus in the mouth, usually in the gums and bone, caused by a bacterial infection. The term gum abscess generally refers to an infection inside the tooth or between the tooth and the gum. Such abscesses usually cause severe pain, redness, swelling, and occasionally a bad taste or bad breath. Most gum abscesses develop as a result of periodontitis, an infection of the gums, or the accumulation of food particles and bacteria beneath the gum line.
A gum abscess is a different type of abscess than an abscess caused by decay inside the tooth, also known as a periapical abscess. Periapical abscesses are an infection that starts inside the tooth and gradually works its way out through the hole at the very tip of the root, spreading to the entire jaw, and is caused by dead and infected nerves inside the tooth.
How to recognize the early signs of gum abscess?

Early signs of a gum abscess can be:
- There may be pain under or around the jaw. You might feel a pulsating ache here.
- Swelling of the cheek or gums may be noticeable. Some people may present with a large lump under the chin.
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or biting pressure.
- There is a bad taste or odor coming from the mouth.
- Swollen lymph glands or lymph nodes under the jaw.
- The patient is experiencing redness and swelling in the gums.
- There can be occasional bleeding in the gums.
- You may notice a pimple-like formation in the mouth indicating that a tooth abscess that was present at the time has found its way out through this area. In this case, the pain may have subsided, but the infection persists.
- The patient has a high fever and is experiencing weakness (lethargic symptoms).
- The patient experiences increased pain when chewing.
Some dental abscesses can develop asymptomatically and can only be recognized at a very advanced stage of the abscess.
How does a gum abscess develop?
A gum abscess is a localized collection of pus that develops as a result of a bacterial infection in the mouth. The development process and causes depend on several factors:
- Bacterial infection: Bacterial infections are the main cause of dental abscesses. These bacteria can reach the pulp of the tooth (the inner part where the nerves are located) in various ways. A dental abscess means the presence of a pus-filled infection inside the tooth or between the tooth and gum.
- Tooth decay and trauma: A crack, fracture or untreated deep decay in the tooth allows bacteria to reach the pulp of the tooth and start an infection.
- Tartar buildup: Tartar that is not removed for a long time sets the stage for bacterial buildup and the development of gum disease, which can trigger the formation of an abscess.
- Periodontal Diseases: Periodontal problems, such as gingivitis and advanced gum disease (periodontitis), can cause bacteria to accumulate in the spaces between the gums and bone, leading to abscess formation. Infection can also reoccur in a tooth that has had a root canal treatment.
- Other Health Conditions: Sometimes other health conditions such as a weak immune system or dry mouth (xerostomia) can also contribute to abscess formation by reducing the body's ability to fight bacteria.
How is a gum abscess diagnosed?
A dental abscess can usually be diagnosed by the dentist just by looking for symptoms like swelling, redness, and tenderness, as well as by taking note of the patient's history of these symptoms. Research indicates that the efficacy of mechanical tests in diagnosing dental abscesses is approximately 50%, while ultrasound can achieve an accuracy of 80%. Although dental abscess is a dental problem whose consequences can be fatal, the diagnosis of some cases in particular requires meticulous work and careful examination.
What are the professional treatment options for gum abscess?

Once the gum abscess is diagnosed, it is usually cleaned with the following treatment methods.
- Abscess opening and drainage: The dentist makes a small incision in the infected area and allows the pus to drain out. Once the pus has drained, the area can be cleaned with sterile saline solution. This relieves pressure and can help the patient to relax. In some cases, a small opening may be left for the new infection to drain.
- Treatment with antibiotics: Antibiotics are often prescribed to control the bacterial infection and prevent it from spreading. However, even if antibiotics are used, the risk of the infection spreading after abscess treatment persists for some time after treatment. Also, antibiotic treatment may not be effective in all apes.
- Extraction: If the tooth is badly damaged or the infection cannot be controlled, it may need to be extracted.
- Root Canal Treatment: If the tooth is salvageable, root canal treatment can be performed. In this procedure, the infected nerves and blood vessels inside the tooth are removed, and the cavity is filled with an inert substance.
How effective are home remedies and pain management techniques?

Popping the abscess or other home remedies may only provide temporary relief. However, here are some home remedies that you can use until you reach a dentist.
- Painkillers: Over-the-counter painkillers (for example, those with anti-inflammatory effects such as ibuprofen, naproxen or paracetamol) can help relieve pain. However, you should not exceed the dosage recommended by the doctor or the package leaflet.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the cheek area can help reduce inflammation and swelling. It states that applying ice for no more than 10-12 minutes can relieve pressure in the area.
- Benzocaine Gel: Topical gels containing benzocaine, available from pharmacies, may temporarily numb the pain.
- Cloves and Clove Oil: There is some information that cloves can reduce pain and inflammation. Clove powder can be mixed with water to form a paste and applied on the abscess.
- Salt Water Gargle: Gargling with warm salt water can help to clean the infected area and provide relief.
- Other home remedies: Various home remedies such as black tea bags, tea tree oil, hydrogen peroxide (not to be swallowed), apple cider vinegar, turmeric and salt, oregano oil, peppermint oil, and sesame seeds are also recommended to relieve symptoms. However, it is important to remember that none of these treat the root cause of the abscess.
How does a gum abscess affect overall health?
If a gum abscess is left untreated, it can cause major complications throughout the body. The following are some of the possible complications that may arise from a gum abscess:
- Spread of Infection into the Bloodstream (Bacteremia): Dental abscesses develop in the soft tissues of the mouth and are in contact with blood vessels. Therefore, there is a risk of the infection spreading into the bloodstream. Drainage at home is not recommended because the infection can spread through the bloodstream and reach other organs.
- Severe Swelling and Airway Problems: Especially neglected abscesses can cause large swelling. If these swellings progress into the airway, they can sometimes block the airway and cause serious breathing problems.
- Spread of infection to the brain: In rare cases, dental infections can spread to the brain and cause life-threatening complications.
- Spread to other teeth and tooth loss: A tooth abscess can not only affect the area where it is located, but can also spread to other teeth, causing them to become infected and lost.
- Cellulitis: If a large tooth abscess is left untreated, it can develop into a common and serious skin infection called cellulitis.
- Fever and Fatigue: People with a tooth abscess may experience high fever and general weakness.
- Difficulty Swallowing and Breathing: Advanced abscesses can cause difficulty opening the mouth, swallowing and breathing. In the presence of such symptoms, urgent medical attention should be sought.
How is a periapical abscess different from a gingival abscess?
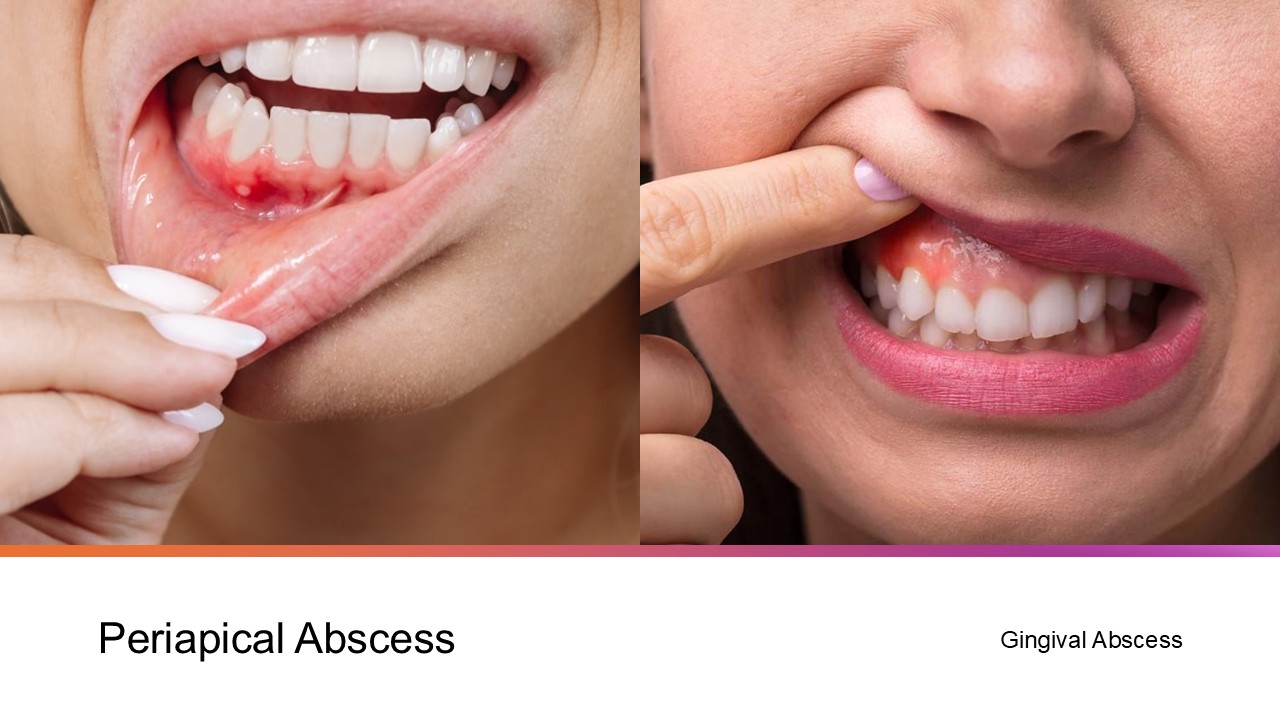
Gum abscess is located at the edge of the gums and causes inflammation. The gums may look red and swollen and sometimes bleed. The main cause of these abscesses is usually due to a local trauma or foreign body entrapment.
On the other hand, a periapical abscess is located at the root tip and under the tooth. The cause is an infection caused by an untreated cavity. Via the oral cavity, germs can infect the tooth pulp, which houses the nerve. This further suggests that infectious bacteria can infiltrate the tooth pulp and initiate the development of an abscess.
What happens if a gum abscess pops?
If a gum abscess pops, pus can drain into the mouth. The drainage can provide temporary relief from pain and pressure. In some people, the treatment may even lead to the illusion that there has been an improvement. However, the source of infection (usually dead and infected nerves or bacteria) is still there. Therefore, even if the abscess bursts, the infection persists and can recur. There is even a risk that the infection will spread to other teeth or parts of the body.
A pimple-like appearance on the gum (fistula) indicates that a tooth abscess that was present at the time has found its way out of that area. In this case, the patient may be relieved that the abscess pressure is gone, but the dead nerves that caused the abscess are still there, and the disease persists.
Is it a good thing if an abscess pops spontaneously?
No, it is not entirely a good thing if an abscess pops. The bursting may result in temporary relief of pain and pressure. However, this does not mean that the infection has disappeared.
How long does it take for a gum abscess to spontaneously rupture?
The time it takes for a gum abscess to spontaneously rupture can vary depending on various factors, such as the person's general oral health, immune system, size, and location of the abscess. Sometimes the abscess drains spontaneously within a few days, but sometimes it takes a week. So, it is not possible to predict when or exactly when the abscess will pops spontaneously.
Should I go to the emergency room if a gum abscess pops?
Usually, when a gum abscess bursts, it is recommended that you first contact your dentist. However, you may need to contact the emergency room if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe facial or neck swelling
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- High fever
- Difficulty opening your mouth
These symptoms may indicate that the infection has spread seriously and requires urgent medical attention.
What happens if you don't go to the dentist right away?
A tooth abscess can develop into multiple problems if the patient does not see a dentist right away. The abscess pus may not be completely removed due to incomplete infection clearance, which can cause the infection to persist or worsen. Without professional intervention, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues, the jawbone, or enter the bloodstream and cause serious systemic problems. Even if there is temporary relief after the eruption, pain, swelling, and discomfort may persist or increase due to untreated infection.
In addition, inadequate cleaning and treatment can increase the risk of abscess recurrence, leading to persistent infections. Finally, delays in treatment can cause damage to the tooth, surrounding gum tissue, or bone structure, leading to the need for more extensive dental treatment. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to seek professional dental help as soon as possible to ensure that the infection is completely cleared and the risks of complications are minimized.
Can popping a gum abscess help?
Spontaneous or unconscious attempts to pop an abscess can contribute to the uncontrolled spread of infection. Therefore, it is safest to consult a dentist and seek professional help in any abscess-related situation. Self-intervention can lead to serious consequences.
FAQs on Gum Abscess
Below you will find frequently asked questions and answers about dental abscesses.
How Do I Know If I Have a Gum Abscess?
Here are symptoms that can help you understand if you have a gum abscess:
- You may notice a pimple-like bump on your gum or near your tooth.
- You may feel pain under or around the jaw.
- You may have swelling in your gums or face.
- You may experience sensitivity to hot, cold or chewing pressure.
- You may have a bad taste or smell in your mouth.
- Your lymph nodes under the jaw may be swollen.
- You may have a fever.
- You may feel lethargic or tired.
- Your gums may look red and swollen and sometimes bleed.
- You may feel a rise in temperature at the site of infection.
- Your pain may increase when you chew.
- You may have difficulty opening your mouth.
What causes recurrent gum abscesses?
There are several possible causes of recurrent gum abscesses:
- There is still some residual infection from the original point of entry. For example, if only the abscess has been drained but the infected tooth or nerve has not been treated.
- Bacteria live inside your jawbone and cannot be completely destroyed by antibiotics alone.
- Dead and infected nerves inside the tooth can be a constant source of infection, like a splinter.
- Untreated caries.
- Trauma
- Infiltration of bacteria under a pre-existing cavity.
- Periodontal diseases (such as gingivitis and periodontitis).
- Tartar that has accumulated for a long time.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Weak immune system.
- Dry mouth (xerostomia).
What are the long-term effects of an untreated gum abscess?
If a gum abscess isnt treated, it can lead to some serious long-term issues. The infection might spread to other parts of the body, cause major complications, lead to tooth loss, block the airway, reach the brain, or even be life-threatening. Plus, theres always a chance the abscess could come back.
Conclusion
As a result, a gum abscess is a serious dental condition that requires immediate professional intervention. While home remedies provide temporary relief, they do not address the underlying infection, making professional care necessary.
Resources:
1- Abscess Management: An Evidence-Based Review for Emergency Medicine Clinicians Samantha Menegas, ∙ Siamak Moayedi, ∙ Mercedes Torres,
